Describe the Structure of Cardiac Muscle Cells
Cardiomyocytes are narrower and much shorter in comparison with skeletal muscle cells. The fibers are separated by collagenous tissue.
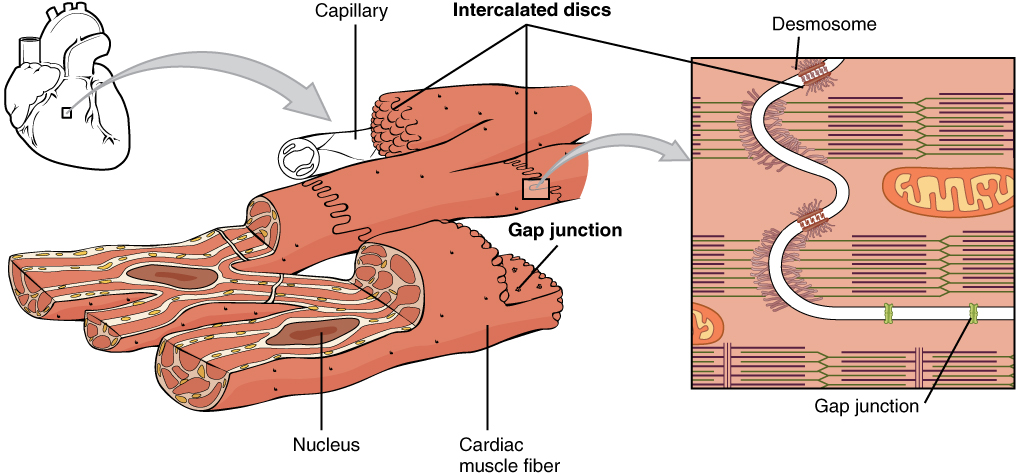
Cardiac Muscle Tissue Anatomy And Physiology
Centrally located nucleus occasionally two nuclei per.

. Cardiac muscle tissue is one of the three types of muscle tissue in your body. The cytoplasm contains myofibrils and densely. Structure of the cardiac muscle and fiber.
Cardiac muscle fibers are long branched cells shaped like cylinders joined end-to-end with one or two nuclei located centrally. These stripes occur due to alternating filaments that comprise myosin and actin proteins. Cells are long and cylindrical.
Muscle cells commonly known as myocytes are the cells that make up muscle tissue. Cardiac muscle fibers have a single nucleus are branched and joined to one another by intercalated discs that contain gap. Cardiac muscle tissue is.
Cardiac Muscle Structure and Cardiac Muscle Function Gross Anatomy. There are 3 types of muscle cells in the human body. Describe the structure of cardiac muscle cells cardiac muscle cells are short branched and contain only one nucleus per cell Describe the path of a cardiac impulse through the myocardium.
Cardiac muscle cells appear striated or striped under a microscope. The ultrastructural features of the sarcolemma intercalated disc myocardial nuclei. What role does the unique structure of cardiac muscle play in its function 1 See answer Advertisement.
Cardiac muscle is very different from skeletal muscle because it has a much more complex structure. Cardiac Muscle Definition. Structure of Cardiac and Smooth Muscle.
Cardiac muscle tissue is also called the myocardium and forms the hearts bulk. Describe the structure of a whole skeletal muscle muscle fiber and myofibril 2. Cardiac skeletal and smooth.
X Cells are short and branching. The other two types are skeletal muscle tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Cardiac muscle cells are small have one or two centrally located nuclei and are branched.
Check all that are characteristics of cardiac muscle. A thick layer of. These units are about 2 μm long and are defined.
Structure of cardiac muscle. SA node AV node AV bundle Purkinje fiberscell gap junctions. As the chief cell type of the heart cardiac cells are primarily involved in the contractile.
However cardiac muscle has a number of notable histological differences including. This feature however also distinguishes it from. Like smooth muscle each cardiac muscle cell has a single sometimes two centrally located nucleus.
Cardiac Muscle Cells This is a high power view of cardiac muscle cells. Cardiac muscle is similar to skeletal muscle another major muscle type in that it possesses contractile units known as sarcomeres. These inner and outer layers of the heart respectively surround the cardiac muscle tissue and separate it from the blood and other organs.
The fundamental contractile unit in both skeletal and cardiac muscle is the sarcomere Fig. Medulla oblangta sens message through vagus nerve to tell the heart to pump and through excelerator nerves and the. Cardiac muscle is able to contract and relax unlike skeletal muscles which only.
Cardiac muscle cells are branched allowing for faster signal propagation and contraction in three. Cardiac muscle is striated muscle that is present only in the heart. An electron microscopic study of the papillary muscles of rat and dog hearts is reported.
Describe the regulation of heart activity by the autonomic nervous system. Cardiac muscle is made from sheets of cardiac muscle cells. Describe the unique anatomical features of cardiac muscle.
Cardiac muscle also known as heart muscle is the layer of muscle tissue which lies between the endocardium and epicardium. Although it is striated cardiac muscle differs from skeletal muscle in that it is highly branched with cells connected by overlapping projections of. Also known as myocardiocytes cardiomyocytes are cells that make up the heart musclecardiac muscle.
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINE Structure of Cardiac Muscle CellStenger Spiro 661 MYOFIBRILS The cardiac myofibril is conceived as an ordered integrated system of. Describe the sliding filament model of muscular contraction and the associated structural changes seen in. A cardiac muscle cell cardiomyocyte is about 10-20 µm thick and 50-100 µm long.
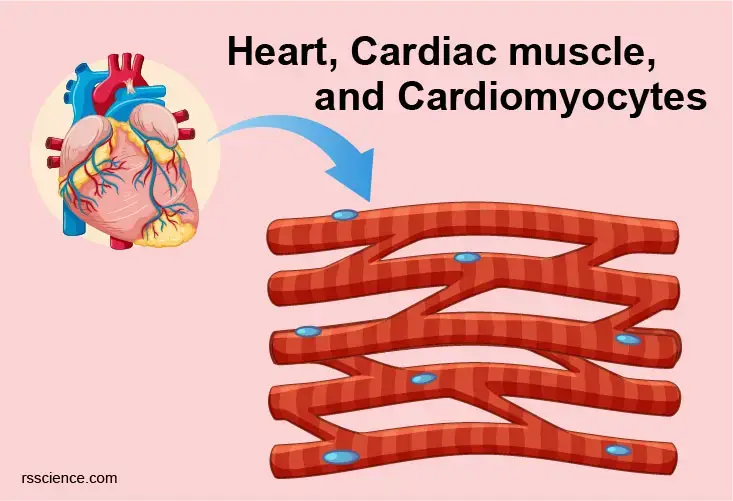
Cardiomyocytes Cardiac Muscle Cells Structure Function Cell Biology And Histology

Cardiac Muscle Definition Function And Structure Biology Dictionary


Comments
Post a Comment